What is Torque Vectoring Technology in Cars and Why It Matters
In simple terms, torque vectoring is a sophisticated drivetrain system that enhances your car's ability to turn more effectively, respond more quickly, and remain more stable, especially at high speeds or in sharp corners. For Indian roads where conditions can shift in a blink—wet patches, potholes, or hairpin bends in the hills—this technology isn’t just about performance; it is about control and confidence.
Let's discuss how this technology works, its various types, the benefits, and why more carmakers are bringing it to a wide range of cars, from SUVs to hatchbacks.
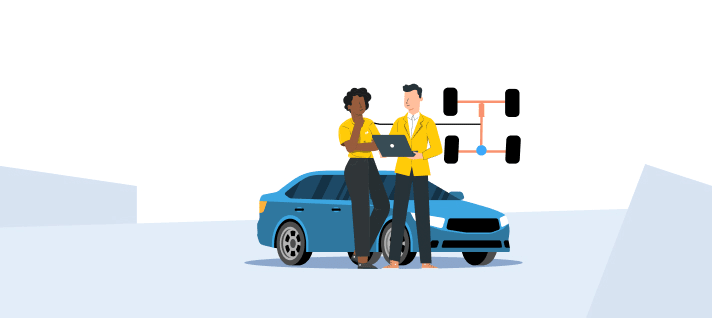
Table of Contents
What Is Torque Vectoring?
You may picture torque vectoring by thinking about how a sprinter uses their legs. One leg pushes harder to keep balance and change direction when you turn. Torque vectoring works on the same concept. It alters the way the engine's rotational force is distributed across the wheels, depending on the driving conditions.
In regular cars, torque is typically distributed evenly across all four wheels. When turning, speeding up, or driving on slick ground, torque vectoring provides more power to the wheel that needs it most. This makes the car more nimble.
If you've ever studied the explanation of torque vectoring, it's likely that you can envision a car operating autonomously, akin to an athlete adjusting their weight during a sprint. It helps your car shift power dynamically to stay in control.
How Does Torque Vectoring Work?
The system operates by utilising sensors, electronic control units (ECUs), and, in some cases, dedicated motors or clutches for each wheel. Here’s a simple overview of how it operates:
- Sensors measure steering angle, throttle position, yaw rate and wheel speed.
- Control units process this data to determine the amount of torque each wheel requires.
- Actuators or differentials then deliver the exact torque to each wheel accordingly.
In front-wheel drive vehicles, it helps minimise understeer. In rear-wheel or all-wheel drive cars, it maximises grip, especially during fast turns or uneven terrain.
So when you’re climbing the ghats in a monsoon in Coorg or navigating a sharp bend in the Western Ghats, torque vectoring ensures your tyres do more than just spin—they grip and guide.
What Are the Types of Torque Vectoring?
Torque vectoring is often mentioned when discussing various types of automotive suspension systems. There are three primary types:
1. Brake-Based Torque Vectoring
It works with an anti-lock braking system (ABS) that prevents the inner wheel from revolving, allowing the outer wheel to generate more torque for quicker turns. Low-cost and common in mid-range cars.
2. Mechanical Torque Vectoring Differentials
Mechanically controls torque with a limited-slip or active differential. This is commonly used in performance cars.
3. Electric Motor-Based Systems
Found in electric vehicles and advanced hybrids. Each wheel may have its own motor, giving you total control. High-end electric all-wheel drive cars feature systems like this.
So, if someone asks what torque vectoring is in cars, the response will be different for an old ICE (internal combustion engine) car and a new EV.
What Are the Advantages of Torque Vectoring?
Now that we've spoken about what torque vectoring is, let's talk about why it's so useful:
- Better handling: You can turn with greater precision and control.
- Greater stability: Less likely to skid or lose control on wet or uneven ground.
- Better traction: This is especially helpful on Indian roads during the rainy season or on rough gravel.
- Responsive driving experience: A car that feels connected and agile, especially when you have to make quick turns.
- Safety boost: It helps prevent cars from spinning out or rolling over when used in conjunction with traction control and Electronic Stability Control (ESC).
Torque vectoring makes a significant difference for city drivers in places like Bengaluru or Mumbai, where traffic jams and sudden changes occur frequently, as well as for highway drivers.
Torque Vectoring in Action: Performance Vehicle Examples
Let’s take a look at real-world applications of torque vectoring:
- Mahindra XUV700: The AWD variant features brake-based torque vectoring, giving it a surprising amount of poise for its size.
- Audi Quattro systems: Many Audi vehicles feature mechanical torque vectoring to make handling better, which makes their big sedans feel more like small cars.
- Tata EVs (Upcoming Platforms): Tata's next EV platforms are likely to use motor-based torque vectoring to make them easier to handle.
- The Porsche Taycan: This supercar model has two motors and a dynamic torque vectoring system, which shows that it handles better than other electric cars.
Understanding torque vectoring can help you make a better choice, whether you're buying a high-end SUV or waiting for the next generation of Indian electric vehicles.
Conclusion
Torque vectoring is now becoming available not just in race cars and luxury SUVs but increasingly in everyday vehicles across India. This shift is wonderful to see, fueled by a greater awareness of safety and a growing enthusiasm for high-performance features.
While these features may enhance driving, safety measures are equally important. That's when Shriram Car Insurance comes in. It provides:
- Affordable yet fully customisable policies
- Zero Depreciation Cover and Roadside Assistance are two popular add-ons.
- Fast claims, no paperwork
- NCB for years without claims
- And a customer-first attitude that knows how to drive on Indian roads
Even the finest cars require sensible insurance coverage.
FAQs
1. Do you need torque vectoring to drive in the city?
Yes, particularly in heavy traffic or when quick lane changes are necessary. It improves grip and stability.
2. Is torque vectoring the same as traction control?
No. Traction control prevents wheels from spinning by applying brakes, whereas torque vectoring directs torque to the wheel with the most grip.
3. Does torque vectoring increase fuel economy?
Not directly, but it enhances the car's performance by offering better grip and minimising wheel spin.
4. Is it possible to add torque vectoring to my current car?
No, it is not possible as it's deeply connected to how a vehicle's suspension and drivetrain work together.



 1602
1602