What Is Regenerative Braking and How It Works
Regenerative braking is a method that lets modern cars, especially electric and hybrid ones, get back energy that would be wasted when they stop. This technique captures energy that would otherwise be lost as heat and converts it into electricity that can be used by the car. This helps the battery charge and improves the car's overall performance.
This innovative concept is transforming the way we think about brakes. It's not only a way to stop; it's also a smart way to save and use energy. For drivers in busy Indian cities, stop-and-go traffic is now more of an opportunity than a problem.
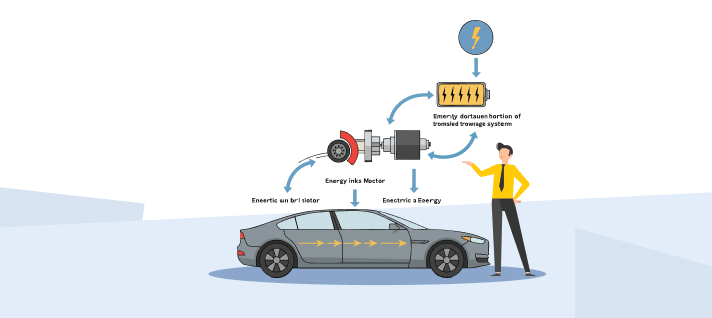
Table of Contents
What Is Regenerative Braking and How Does It Work?
What is regenerative braking at its most basic level? During braking, the electric motor of a car works as a generator in this process. In a car with regenerative braking, the electric motor slows down the car when you press the brake pedal instead of relying only on friction brakes.
This process reverses the motor's direction, converting movement into electrical energy that is transferred back to the battery. Many EVs and hybrids use this technique.
Essential elements included:
- Electric motor/generator: Performs the dual function of energy recovery and propulsion
- Battery pack: Stores the energy that was recovered
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): This part controls when and how the system functions.
How Does Regenerative Braking Provide Electricity?
Your vehicle converts motion into electricity every time you slow down by using the regenerative braking system. This approach is based on a simple idea from physics: using a generator to transform mechanical motion into electrical power.
In regular braking systems, this energy is released as heat because of friction. However, with regenerative braking, the motor operates in reverse, generating electricity instead. The electricity is transferred to the car's high-voltage battery, where it is stored for later use. It can be used in running the electric drivetrain or even the air conditioning.
This is especially helpful when driving in cities like Mumbai or Bengaluru, where frequent stops provide the battery with numerous opportunities to recharge.
What Are the Types of Regenerative Braking?
These are the main kinds used in vehicles today:
1. Electric regenerative braking
This technology is primarily used in electric and hybrid vehicles. It helps brake by transforming the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy via the electric motor.
2. Hydraulic Regenerative Braking
This system, mainly used in buses and commercial vehicles, replaces a traditional battery with an integrated hydraulic energy storage system.
3. Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems (KERS)
Formula 1 popularised KERS, which stores braking energy in a flywheel or battery and then uses it to accelerate. Many high-end cars feature this technology to enhance efficiency.
- Even though these regenerative braking systems have varied uses, they all work on the same basic idea: changing energy and using it again.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative brakes, like any other automotive technology, have their pros and cons.
Pros
- More efficient, especially in heavy traffic where cars often have to start and stop because they are travelling slowly or are stuck in bumper-to-bumper traffic on main roadways.
- Less wear on the brakes: Lower servicing costs come from using friction brakes less often.
- Longer driving range: This is especially useful for electric cars because it saves battery power and helps the car cover more distance for the same level of charging - similar to mileage in a traditional petrol or diesel car.
Cons
- Low efficiency at high speeds: Best suited for moderate-speed deceleration or urban environments
- Not a full replacement: Still uses regular brakes to stop in an emergency
- Variable feel: Drivers may require time to get adjusted to the altered brake sensations.
Combined with careful driving, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks on Indian urban roads.
What is The Future of Regenerative Braking?
Regenerative braking is expected to play a crucial role in improving both the efficiency and appeal of electric vehicles (EVs) as India progresses toward adopting electric mobility.
Here are some future prospects:
- AI integration: Predictive braking systems that learn how you drive
- Energy sharing networks: In the future, electric vehicles (EVs) may be able to supply energy to the grid.
- Higher efficiency: As battery and motor technologies continue to evolve, they will become more efficient.
India is planning to achieve a 30% electric vehicle penetration rate by 2030, as stated by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH). To get there, we need technologies like regenerative braking in cars.
Final Thoughts
Regenerative braking is more than just a high-tech brake; it's also an energy-efficient system that converts your car's motion into electricity. Adopting regenerative braking is a smart choice for Indian drivers seeking to save money on petrol, reduce maintenance expenses, and support sustainable driving.
Your Car Insurance plan should also adapt to the growing sophistication of modern vehicles. Shriram Car Insurance provides tailored, affordable coverage with benefits including minimal paperwork, quick claims processing, and add-ons such as Zero Depreciation and Engine Protection. These features can help your policy better cover electric and hybrid vehicles. Shriram Car Insurance provides smart protection that adjusts to the modern features of your vehicle, regardless of the type of car you own.
FAQs
1. Is regenerative braking available in all cars?
No, it's mostly found in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid automobiles. It is also found in certain high-end performance cars.
2. Does regenerative braking affect driving range?
Yes. It extends the driving range of electric vehicles (EVs). It makes hybrid vehicles more fuel-efficient by capturing energy during braking.
3. Do I still need ordinary brakes if I have regenerative braking?
Yes. The system is designed to supplement friction brakes, rather than serve as a complete replacement, particularly in emergency situations.
4. How effective is regenerative braking during highway driving?
It doesn't work as well at high speeds or on roads, where you don't have to stop as often. It functions most effectively in urban traffic.
5. Can regenerative braking fail?
Though uncommon, it is capable of failing, just like any mechanical system. That's why cars still have traditional brakes as a backup.



 2744
2744