Why Does a Car Stop When You Apply the Brakes? Explained Simply
You’re driving at your usual speed, but you abruptly apply the brakes to avoid hitting someone who suddenly appears on the road ahead. While pressing the brakes certainly stops the vehicle, have you ever wondered how your foot’s little pressure can stop a multi-ton vehicle?
The answer is it doesn’t. It’s the hydraulic brake system which multiplies your foot pressure to create friction between the wheels and the road. This pressure engages the car’s brake pads, which produce the friction required to slow or stop a vehicle.
The science behind ‘how car brakes work?’ is fascinating, but it can be too technical for people to understand. Hence, in this blog, we’ve simplified the mechanism that runs your car’s braking system so you can better understand your car.
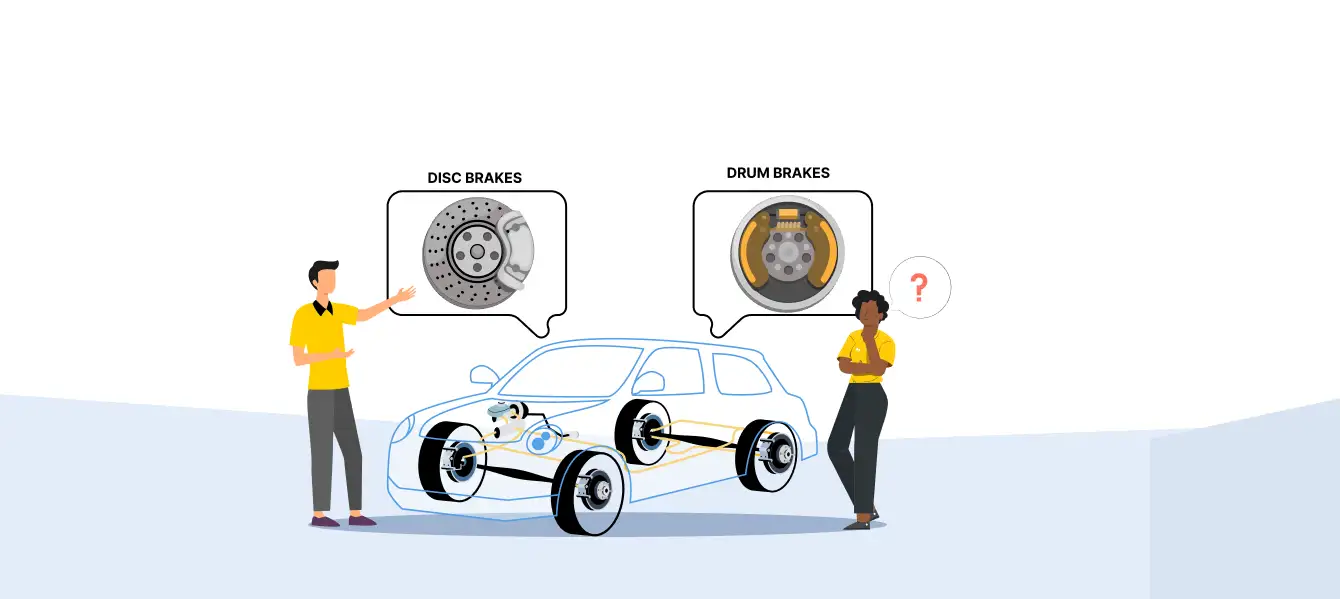
Table of Contents
Understanding the Car Braking System
Understanding the car's braking system requires a clear understanding of the keybrake components. Hence, first understand the main parts listed below:
-
Brake Pedal
The brake pedal is the first component that begins the car’s stopping process. It helps register the driver’s input as soon as the pedal is pressed.
-
Brake Booster
It’s a hydraulic-powered device which multiplies the force you apply to the brake pedal.
-
Master Cylinder
The master cylinder converts the multiplied force into hydraulic pressure. The conversion takes shape as brake fluid is pushed into the brake lines.
-
Brake Lines
These tubes carry pressurised brake fluid to the wheels through the master cylinder.
-
Calliper
It’s a clamp-like part that houses the brake pads and is pushed by the hydraulic pressure.
-
Brake Pads
Brake pads are friction materials which the calliper presses against the brake rotor.
-
Brake Rotor
It’s a disc attached to the wheel hub. You can see it spinning with the wheel.
-
Brake Drums
You can find brake drums in some rear wheels. Instead of squeezing the brake disc, the brake shoes are expanded inside these drums to create friction.
Now that you’re aware of the main car brake components, let’s understand the mechanism behind how car brakes work. As you press the brake pedal, the master cylinder sends pressurised brake fluid through the brake lines to the wheels.
This brake fluid pressure activates the calliper, which squeezes the brake pads against a spinning brake disc attached to the wheels. It creates the friction needed to stop a car.
The Role of Friction in Stopping the Car
Your car cannot stop without sufficient friction, no matter how hard you press the brake pedal. Friction stops the car in two ways. Firstly, when you press the brake pedal, the brake pads are forced against the brake discs/ brake drums. It generates kinetic friction required to resist the wheel’s rotation, making it slow down.
Secondly, as the wheels slow down, the friction between the tyres and the road surface prevents them from skidding. It generates the force needed to bring the car to a halt. The easiest way to understand this process is by comparing it with the process of rubbing your palms together in a fast manner.
Once you start rubbing your palms quickly, it produces extreme heat and resistance. The same force works inside the brakes, but on a much stronger level. If you remove friction from the process, the wheels will continue to spin freely, no matter how hard you press the brake pedal. Simply put, friction converts motion into resistance. It gives drivers control and stopping power over their car.
Advanced Systems like Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS)
The ABS braking system is a safety system designed to help you maintain control during hard braking. If you notice someone applying the brakes forcefully, you will find that the wheels stop rotating, whereas the car may continue to move in some cases.
It leads to the wheels ‘locking up,’ and increasing the chances of skidding on roads. Whenever the wheels lock up, you will find it challenging to steer or avoid obstacles on the road. It is where the ABS braking system comes to your rescue. It prevents skidding by rapidly pulsing the brakes.
It makes the wheels rotate just enough to maintain grip. You may feel a vibration in the pedal during ABS action, but it’s normal. This system doesn’t reduce braking power, but ensures the car’s tyres remain connected to the road, allowing you to enjoy better stability and steering control during emergencies.
Energy Conversion during Braking
A moving car carries kinetic energy, which increases with speed. Applying the brakes won’t erase this energy, but it will transform it. When the brake pad in the car’s braking system presses against the brake rotor, a friction is generated, which converts the car’s kinetic energy into heat.
It is why car brake components get hot after repeated braking. This heat is released into the air, so the car can slow down safely. If you’re still confused, consider the car braking system as a converter, which converts movement into heat. It helps the wheels lose speed securely.
Understanding this will also help you understand why brake components wear out over time. They constantly absorb and disperse energy through friction, which may require faster replacement.
Importance of Regular Brake Maintenance
Car brake components can wear out over time, raising serious safety concerns. Hence, anyone serious about their and their car’s safety should invest in regular brake maintenance. It will prevent road accidents and costly future repairs and replacements. Even if your hydraulic brakes work perfectly today, they may stop functioning abruptly for several reasons.
For instance, the brake discs may develop uneven surfaces due to repeated braking. It can affect the smooth braking process. Brake fluid may also absorb moisture over time, reducing its ability to transfer pressure effectively. With regular maintenance, you don’t have to worry about such issues.
Conclusion
Braking may feel like a quick, simple action, but there’s a well-oiled mechanism that controls how car brakes work. The system magnifies your foot pressure and converts it into friction, which securely slows and stops your car. You can go through the simplified breakdown of the entire process shared in this blog whenever you need clarity.
Some people fear that their car’s braking system may not always function properly, and can potentially lead to accidents and vehicle damage. If you have similar thoughts, consider insuring your car under a Comprehensive Car Insurance policy with generous coverage.
The Shriram Car Insurance provides greater coverage at affordable premiums. You can easily personalise the coverage using different add-on covers.
FAQs
1.How do car brakes stop a vehicle?
Car brakes use hydraulic pressure to stop a vehicle. The car’s braking system multiplies your foot pressure to generate enough friction, which can bring the car to a stop.
2.What components make up a car’s braking system?
A car’s braking system is made up of several parts. But components, such as a brake pedal, master cylinder, brake fluid, and calliper are the most important. All these parts work together to safely slow the car.
3.What is the function of brake fluid?
The car’s braking system uses this fluid to transfer pressure from the brake pedal to the wheels effortlessly.
4.How does ABS improve braking safety?
It prevents the car’s wheels from locking during hard braking. ABS reduces the instances of skidding by rapidly pulsing the brakes.
5.Why is brake maintenance important?
Brake maintenance is vital because brake components may wear out over time. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent brake malfunctions. Something as simple as routine brake maintenance can keep you and other passengers safe during hard braking.



 855
855